Fluorinated Cation Exchange Membrane Technology Improves Electrolysis and Electrodialysis Processes

Reading Time: 3 minutes
Membrane-based electrolysis and electrodialysis use an electrical field to separate charged and non-charged molecules. Cation exchange membranes are used to produce or recover chemicals by electrolysis processes, and industrial processes require membranes that are highly resistant to chemicals. Fluorinated cation exchange membranes with a sulfonic acid group provide this resistance and other performance advantages like mechanical strength. 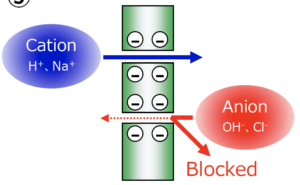
Our FORBLUE™ S-Series ion exchange membranes are based on a fluorinated base polymer, which enables them to survive in harsh environments. It is also possible to increase their performance strength, stability and handling ease by incorporating special PTFE fiber reinforcement into a sulfonic acid polymer film.
Applications for S-Series membranes include:
Alkaline water electrolysis and PEM water electrolysis
Today, there is a growing use of hydrogen as an energy resource. Alkaline and PEM water electrolysis are highly efficient ways to produce hydrogen. A water source is fed into an electrolytic cell and current is passed through the water. Hydrogen forms on the anode and is collected as a product. S-Series membranes are used to separate the anodic chamber from the cathodic chamber to prevent crossover, which adversely affects the efficiency of the process. The anodic side of the cell is acidic, and the cathodic side of the cell is basic, so it is important to use a chemically resistant membrane.
Redox flow batteries
Redox flow batteries are safe, long-life and large-capacity rechargeable batteries. These electrochemical cells generate chemical energy when two chemical components are dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides of a membrane. While both of these liquids circulate in their respective spaces, ion exchange occurs through the membrane, accompanied by a flow of electric current. The chemicals used in this process are corrosive and require a chemically resistant membrane with high ion selectivity and low resistance  properties material. S-Series membranes perform well in this application.
properties material. S-Series membranes perform well in this application.
Production and recovery of chemicals by electrolysis processes
Cation exchange membranes used in electrolysis processes to produce or recover chemicals need to be durable against acid or alkaline solutions. One such example is the electrolytic production of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH). TMAH is frequently used in the electronics industry as a developer or cleaner in etching and stripping mixtures. Producing TMAH requires stacking membranes in an electrolytic cell. When current is applied to the stack, the anions flow through anionic membranes while the cations flow through cationic membranes. Products are either depleted or concentrated, depending on the desired result. S-Series membranes are ideal for production of TMAH because it a very harsh base material.
Additional S-Series membrane benefits
- High cation-selective permeability
- High ion exchange capacity for very low resistance with high ion selectivity
- Excellent separation
- Outstanding current carrying capability
- Low electric resistance for energy savings
S-Series wet and dry membranes are available in a wide array of thicknesses and with ion exchange capacities from 1.0 to 1.25 meq/g.
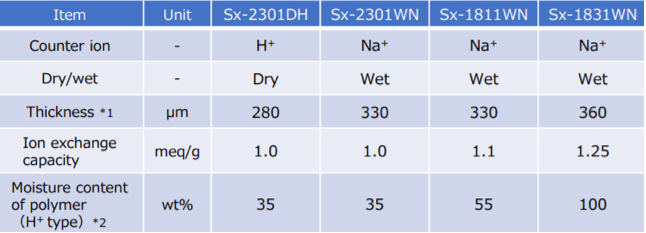
For more information about FORBLUE S-Series membranes, download this data sheet or contact an AGC representative.
 English
English