Fluoroelastomer Rubber Performs in Demanding Applications

Reading Time: 5 minutes
Fluoroelastomer rubber is synthetic rubber that is formulated with fluoropolymers. It is used to enhance the properties of fabricated parts.
Compared to silicon and other synthetic rubbers, fluoroelastomer rubber displays exceptional resistance to high temperatures and a wide range of chemicals, as well as various fluids and oils. These attributes make fluoroelastomers popular for high-performance applications that require component reliability and durability.
However, the different terminologies and classifications used can lead to confusion about what exactly fluoroelastomer rubber is, so we will attempt to answer the question, “What is a fluoroelastomer rubber?”
Characteristics of Fluoroelastomer Rubber
These synthetic rubbers are made up of fluorine, carbon and hydrogen. Their unique chemical composition, specifically the high ratio of fluorine to hydrogen, and their distinctive molecular structure, is what endows fluoroelastomers with their notable resistance qualities.
Outstanding characteristics of fluoroelastomer rubber:
- High heat resistance up to 200 °C (392 °F) and in some formulations up to 300 °C (572 °F) when compared with other elastomers
- High repellency to chemicals including aggressive solvents, fuels, oil, ethanol, concentrated acids and alkalis (depending on formulations)
- Resistance to silicone oils and greases
- Low gas absorption
- Slow compression set at elevated temperatures
- Weather, UV and ozone resistance
- High durability and strength
- Steam resistance
- High protection from oxidation and degradation
- Resistance to aging for long-term reliability that reduces maintenance and prevents unscheduled downtime
To gain an even deeper understanding of “What is a fluoroelastomer rubber?,” read on about the different classifications of this polymer. Their differing compositions based on fluorine content and monomer combinations give them unique qualities that are ideal for specific applications.
Fluoroelastomer Classifications
The industry recognizes the following three classifications of fluoroelastomers, distinguished by their composition and properties:
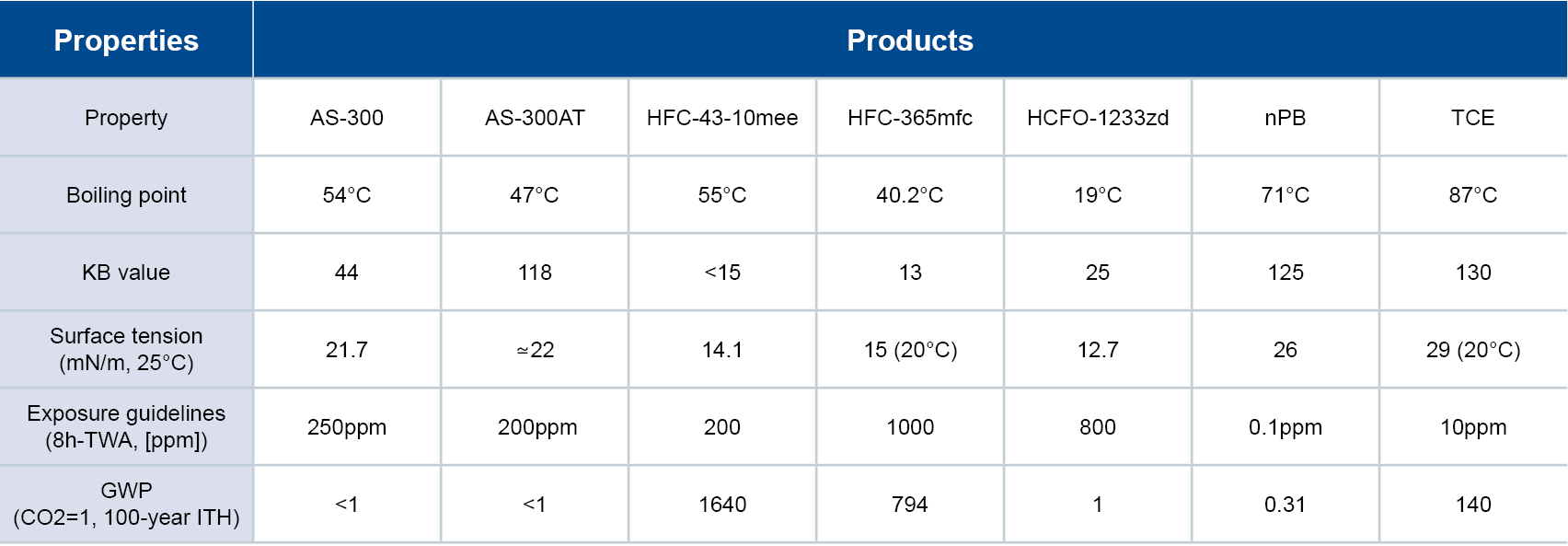
- FPM/FKM: This type was one of the first on the market and represents over 80% of fluoroelastomers. It strikes a balance between performance and cost with a fluorine content ranging from 66% to 70%. Composed of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene copolymers, FKM comes in five different grades based on monomer mix. It’s referred to as FKM by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM D1418) and as FPM by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- FFKM:Also known as perfluoroelastomer, this variant contains over 70% fluorine, enabling it to withstand temperatures up to 325 °C and maintain almost universal chemical compatibility. It offers superior performance but at a higher cost, making it suitable for specialized uses.
- FEPM: A copolymer of propylene and tetrafluoroethylene, this peroxide cross-linked elastomer has a fluorine content of around 54%. It’s competitively priced and offers distinctive resistance to certain chemicals, excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation, leading to new uses for fluoroelastomers.
Classifications of fluoroelastomers are associated with certain brands. For instance, FEPM is known by the brand name AFLAS. Categorized within ASTM D1418-01 as FEPM, AFLAS fluoroelastomers possess unique properties over conventional FKM-type fluoroelastomers to excel in demanding automotive applications.
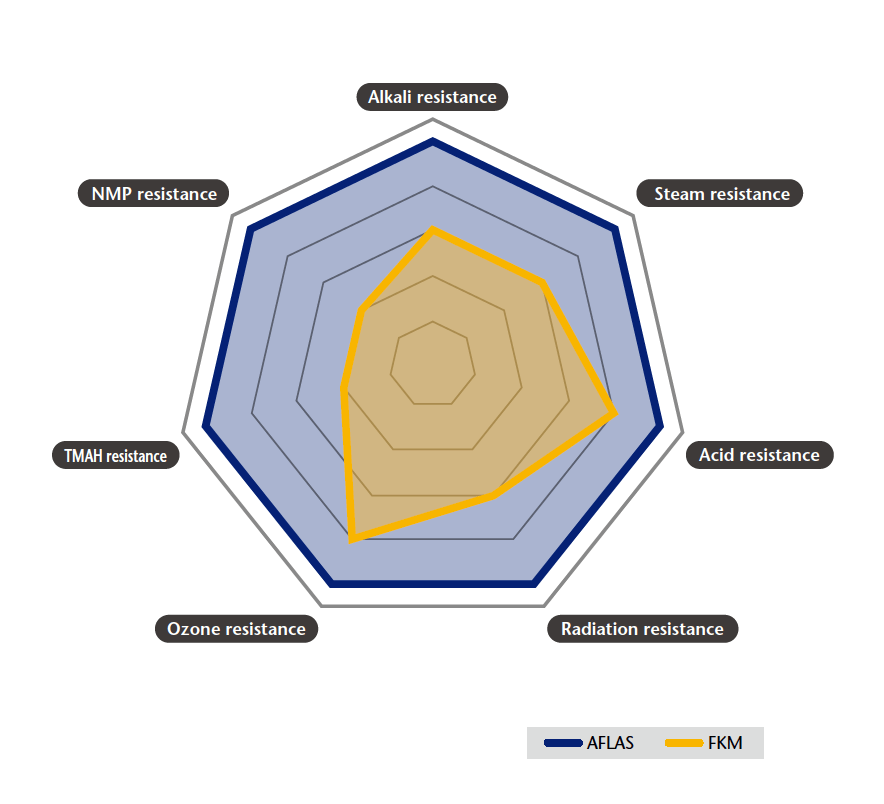
So, depending on the brand, you may get different answers to “What is a fluorolastomer rubber?”
Applications of Fluoroelastomer Rubber
According to Global News Wire, the fluoroelastomer market size is estimated to grow to $2 billion by 2030. Their excellent chemical and heat resistance has driven market growth in various industries.
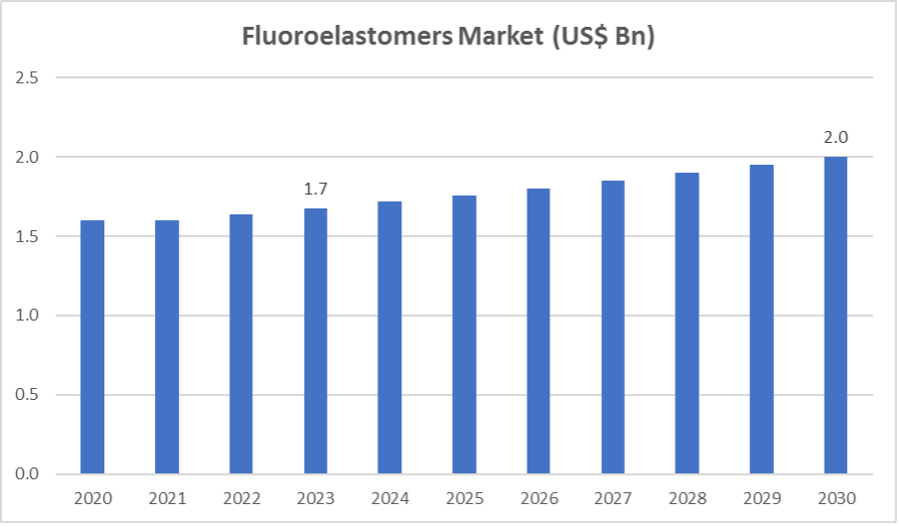
Initially created for seals and O-rings in aerospace hydraulics, 60% of fluoroelastomers are now used in the automotive industry. Aerospace now accounts for 17% of their use, with chemical and petrochemical industries making up 12%.

Parts molded from fluoroelastomers are critical for safe and reliable operations as well as long-term wear against the environment. This versatile synthetic rubber is crafted into a variety of dimensions, densities and hues to create components for:
Automotive
- Seals for transmission and pinion shafts
- Fuel lines
- Seals and O-rings for fuel injectors
- Cylinder head gaskets
- Pump diaphragms
- Heat-sealable tubing for wire insulation
- Electrical wire and cable
Aerospace
- Seals for firewalls
- Stems and seals for valves
- Gaskets for manifolds
- Flexible hoses
- O-rings for fuel and hydraulic systems
- Heat-sealable tubing for wire insulation
Petrochemical
- Various types of seals
- Gaskets
- Linings for pumps
- High-voltage cables
- Components for oil rigs

Industrial
- Electrical connectors
- Valve liners
- O-ring seals
- Fuel joints
Continued advancements in fluoroelastomer material technology are extending its use into new applications and markets including food and beverage and semiconductor wafer fabrication.
Selecting the Right Fluoroelastomer
When selecting a fluoroelastomer, assess the specific needs of the application including:
- Thermal stability: Can it perform within the required temperature range without losing properties?
- Chemical compatibility: Are there any gases or chemicals involved that could diminish the elastomer’s performance or cause degradation?
- Permeation resistance: Tighter restrictions on auto evaporative emissions make this measurement increasingly important.
- Flexibility: Does the material need to flex in temperature cycling?
- Service life/durability: What is the expected lifespan when subjected to operational conditions, such as high heat?
- Manufacturing process: How well does the material handle various manufacturing techniques like extrusion or injection and compression molding?
- Shape of the molded parts: Is the material capable of achieving the desired geometry?
- Budget: Does the cost match its value in performance? Should you opt for a standard or a premium grade for enhanced properties?
After selecting a fluoroelastomer, it is important to perform tests and evaluations to verify its compatibility with the application’s demands. Avoid cheaper blends with inferior qualities and consider specialized grades for heightened performance.
For example, several AFLAS grades are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for food contact so that they work in food processing applications where heat or aggressive chemicals can degrade other rubbers. The AFLAS latex series features liquid grades used for binders and coating materials, while the AFLAS FFKM series offers high-temperature durability for ultra-hot temperatures.
Always consult a materials expert who understands the complexities of choosing the right material. AGC Chemicals formulates AFLAS resins and provides samples for testing. AGC also has testing capabilities to evaluate specific grades before purchase.
For more information on AFLAS fluoroelastomer rubbers or to ask questions about “What is a fluoroelastomer rubber?”, contact us.
 English
English