Advantages of Silica Gels for HPLC Packing Applications
Reading Time: 3 minutes
Silica gel is one of the most versatile and effective agents used in chromatography today, making it also one of the most popular. It is a polar absorbent with slight acidity, enabling it to absorb basic contents in a material that needs separation during chromatography, while also remaining neutral and maintaining its own structure throughout the process.
For high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), in particular, accuracy is king. Column packing, separation and purification influence accuracy, making the quality of the silica gel used an incredibly important factor when processing difficult separations.
AGC Chemicals Americas provides high-purity, porous silica gel with low moisture content and high lot-to-lot consistency. When used as a packing medium, this microspherical gel enables a separation process that is highly reproducible.
What is Silica Gel?
Silica gel is an amorphous silicic acid polymer represented as SiO2-nH2O. Three types of silanol groups are on the surface of silica gel: isolated, vicinal and germinal. Silanol groups usually exhibit weak acidity and serve as absorption-active sites. Chemical bonding is used to add a stationary phase functional group to the silica gel particle. For example, M.S.GEL™ particles can be bonded with C4, C8, C18, NH2, SP, CM, epoxy, diol and phenyl.
Ideal Applications for Microsphere Gels
- HPLC packings
- Process chromatography
- Separation media for proteins, peptides, and active pharmaceutical ingredients
- Adsorption and removal of ionized compounds from organic solvents
- Medical & Pharmaceutical
- Antibody purification
- Insulin purification
- CoQ10 separation
- Hemodiafiltration
- Industrial
- Liquid crystal purification
- Metal scavenger
- Food & Beverage
- Residual pesticide analysis
- Material analysis
- Environmental Research
- Water quality
- Soil
- Atmosphere
When selecting silica gel, keep in mind the three physical properties that influence separation: particle shape, particle size and pore diameter.
Particle Shape
Particle shape can really impact separation efficiency. The more spherical the shape, the more homogenous the packing characteristics and the less solvent required for the process. M.S.GEL particles have a near-perfect spherical shape that is free from cavities and cracks. This provides three advantages over plastic beads:
- Higher loading capacity
- Lower column back pressure
- Better component separation
Particle Size and Pore Diameter
Particle size determines the efficiency of the silica material. Smaller particles produce more efficient separations. Small particles (< 2 µm) are most commonly used for high-resolution separations using longer columns or high-speed separations using shorter columns.
Pore diameter is used to control retention. Silica particles used in chromatography have a high surface area, a requirement for good analytical retention. The majority of a particle’s surface area is contained in the internal pore structure of the silica particles. The surface area of the silica particle is inversely proportional to the pore diameter, meaning smaller pores tend to be deeper with more surface area compared to larger pores which tend to be shallower and provide less surface area.
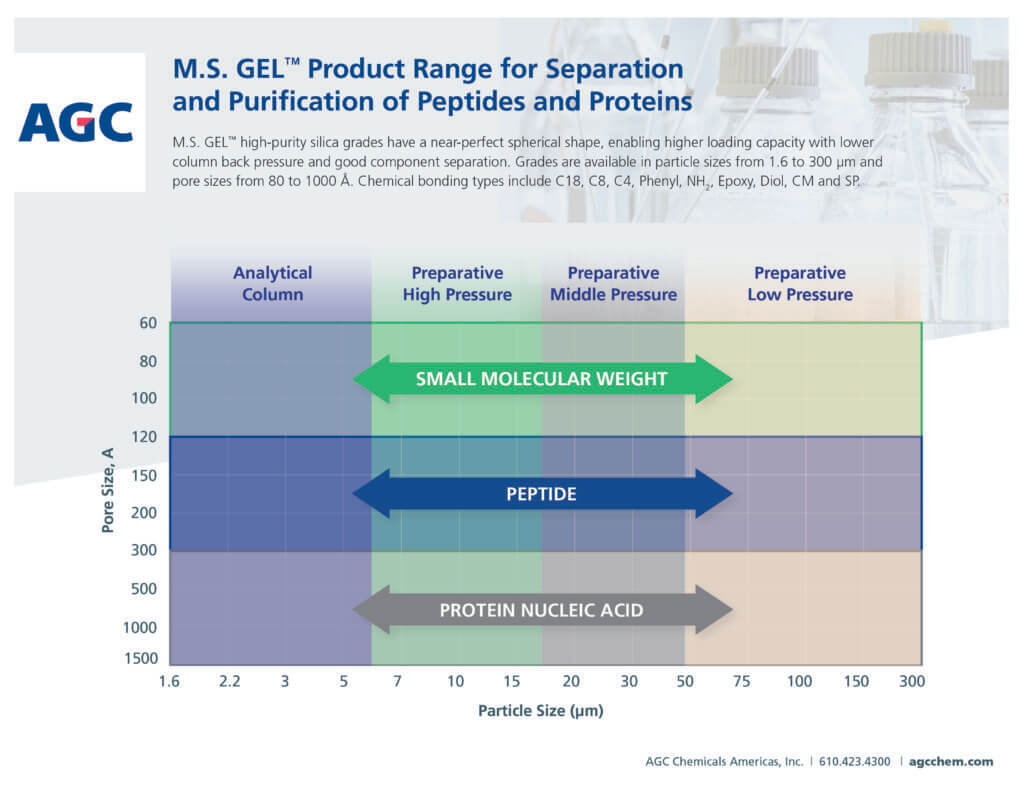
AGC provides a wide range of size options for HPLC. M.S.GEL microspheres are available in particle sizes from 1.6 to 300 µm, specific surface areas from 30 to 900 m2/g and pore sizes from 60 to 1500 Å. They are available for analytical columns and high-, middle- and low-pressure preparative applications.
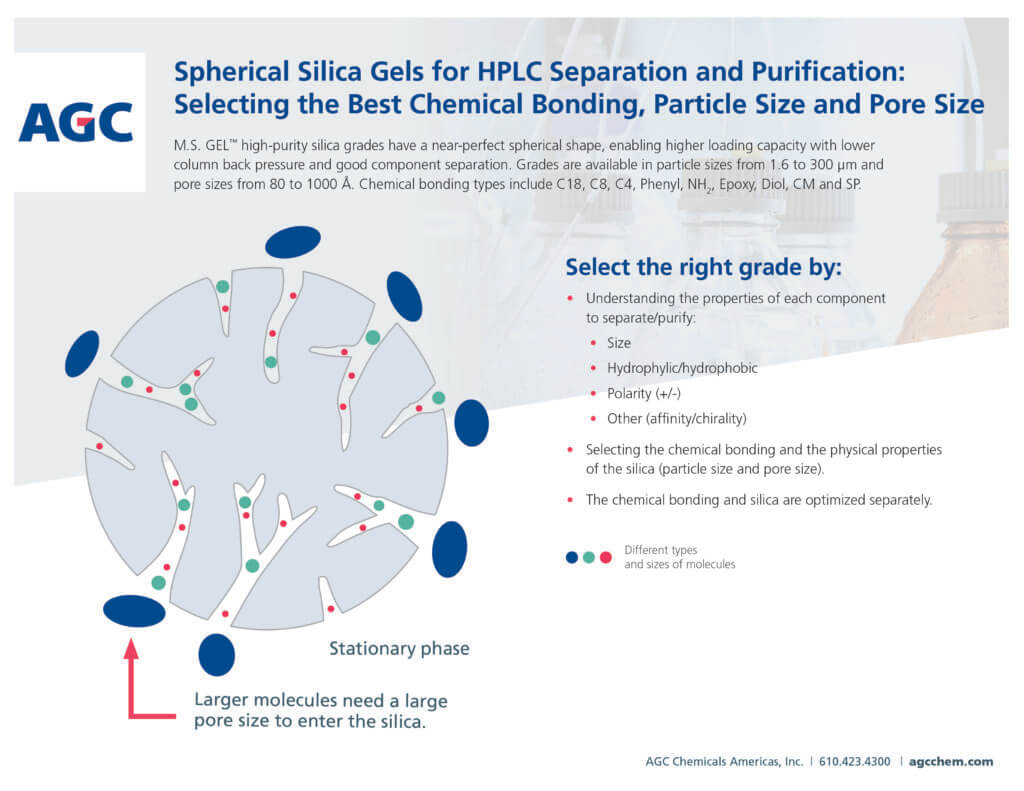
Selecting the Best Grade for your Application
When selecting HPLC packings, it is important to understand the properties of each component to separate or purify. These components include their size, whether they are hydrophilic or hydrophobic, their polarity and their affinity/chirality. It is important to select the chemical bonding and physical properties of the silica based on the material being separated. For example, large molecules (illustrated below in blue) can’t enter the silica particles unless the silica has a large pore size. The chemical bonding and silica are optimized separately.
The experts at AGC are here to help you find the right-sized silica gel for your testing needs. Contact us today to learn more.
 English
English