SOLESPHERE Fine Silica Particles Enhance 3D Printing Resins Used in Different Processes
Reading Time: 3 minutes
3D printing has completely transformed our world with its countless applications. It’s not just about rapid prototypes anymore. Now, we’re using it for everything from crafting prosthetics and medical gadgets to creating stylish clothes and educational tools.
3D printing resins are a key component. They provide the desirable characteristics that regular fillers just can’t match. They’re what enable us to create intricate, personalized, three-dimensional products and components.
What is 3D Printing?
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing is a process that builds three-dimensional objects from a digital blueprint. Here’s how it works: Layers of 3D printing resins and other additives are stacked up to form an object with a specific shape, size and texture.
3D printing is efficient. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, where materials are carved away from a block or shaped using a mold, 3D printing adds material exactly where it’s needed, layer by layer. This not only speeds up the production process but also minimizes waste, since materials are only used as required.
Additive manufacturing also reduces prototyping costs by eliminating the need for expensive molds. Creating a mold for injection molding can be costly and time-consuming. But with 3D printing, users can easily tweak designs during the development phase by simply adjusting the digital file.
3D printing also offers a cost-effective way to produce small batches of products, cutting down on excess inventory and manufacturing expenses.
The 3D Printing Market on the Rise
Thanks to new applications emerging in defense, breakthroughs in electronics, and strides in manufacturing, the 3D printing sector is experiencing significant growth. Research sources estimate its value will soar to $31 billion by the close of 2024. Market insights project that by 2032, the 3D printing market will surge to $108.11 billion, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 20.5% from 2024 to 2031. Continued innovation and enhanced efficiency will support this dynamic expansion well into the future.
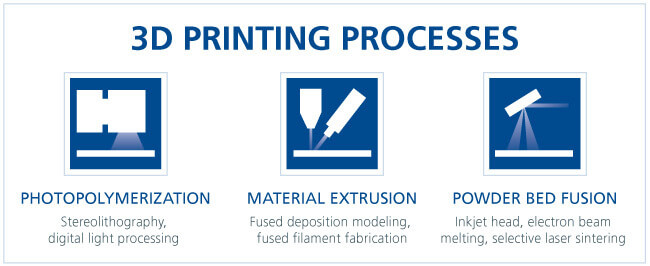
3D Manufacturing Processes
Since its inception, 3D printing has diversified into various manufacturing methods, including photopolymerization, material extrusion and powder bed fusion. Photopolymerization is one of the most widely adopted methods, encompassing stereolithography (SL/SLA) and digital light processing (DLP). These processes use liquid 3D printing resins, which solidify under a light source to create three-dimensional printed objects. In the case of SLA, lasers cure liquid resin into materials, while DLP employs shorter wavelength light for resin curing.
Material extrusion also uses 3D printing resins or photopolymers that harden under UV light to build 3D components. One variant, fused deposition modeling (FDM), alternatively known as fused filament fabrication, offers low-cost prototyping of simple parts but does not offer the resolution or accuracy of SLA techniques.
Powder bed fusion, on the other hand, uses a laser to fuse atomized powder particles. This additive manufacturing technology encompasses diverse methods such as direct metal laser sintering, electron beam melting and selective laser sintering. While more expensive, this method enables the production of intricately shaped parts using polymers and metals.
Fine Silica Particles Enhance 3D Printing Resins
In resin-based 3D printing processes, four main types of resins are commonly used: acrylates, methacrylates, epoxides and polyesters. These resins are often formulated with specialized fillers to enhance their performance. Manufacturers are continuously exploring ways to cut costs and enhance performance, aiming to mimic the characteristics of the final product.
Integrating RESIFA™ SOLESPHERE™ microspheres into fillers can address these goals, enhancing product quality, performance and processing efficiency. Additionally, incorporating silica particles can help reduce costs, especially considering the typically high expense of 3D print build resins.
Available in various particle sizes and porosities, these highly spherical and exceptionally pure fine silica microspheres enhance properties like tensile and flexural strength, dimensional stability and thermal resistance without the processing challenges typically associated with fillers—even when used at loading levels exceeding 10%.
Additional benefits include:
- Enhanced thermal resistance and improved heat deflection temperature.
- Consistently uniform particle size distribution leading to more reliable batches.
- Compatibility with a wide range of materials including acrylates, methacrylates, epoxies, polyesters, nylon, ABS and other resin compounds.
- Easy dispersion within a polymer matrix.
- Prevention of soft polymer blocking in powder fusion processes.
- Active chemical surface facilitating strong chemical bonding and interactions with resins and other fillers.
- Applicability as a filler for additive manufacturing, with loadings ranging from 3 to 50% by weight.
To learn more about RESIFA SOLESPHERE fine silica for 3D printing resin formulations, visit https://www.agcchem.com/products/fine-silica-gels-3d-printing-resins/.
 English
English