PTFE Micropowders Add High Resistance and Lubrication Properties to Thermoplastic Parts, Rubbers, Inks, Paint and Oils

Reading Time: 4 minutes
PTFE micropowders evolved out of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) coating materials that have been used for a long time in non-stick cookware. However, their uses extend beyond that. PTFE has many useful properties such as being resistant to water, heat, electricity, and friction.
Because of these properties, PTFE can improve the durability and strength of thermoplastic and elastomer products. It can also enhance the performance of inks, coatings, and specialty oils when used as an additive.
What is PTFE?
The synthetic fluoropolymer PTFE was accidentally discovered by a DuPont scientist over eighty years ago while developing a new refrigerant. It has an extremely low coefficient of friction, which makes it the slipperiest material known and perfect for non-stick applications. It’s classified as a thermoplastic and can tolerate wider temperature ranges (-180°C to 250°C) than other insulators.
Manufacturers typically use PTFE as a granular powder to add to other materials. The controlled emulsion polymerization process mills PTFE into white particles of various sizes. This PTFE micropowder can be added to rubber or plastics or dispersed as a dry lubricant to improve the friction and wear of the base material.
Virgin PTFE powders, made from new rather than recycled PTFE, provide the highest quality and consistent performance. The Food and Drug Administration approves virgin PTFE for use in the food, beverage and pharmaceutical industries.
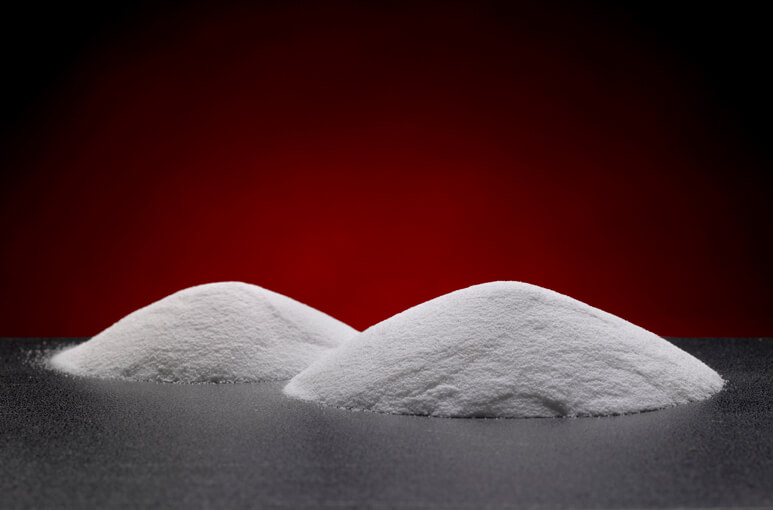

PTFE Compound Structure
The chemical structure of a PTFE compound is shown in this diagram.
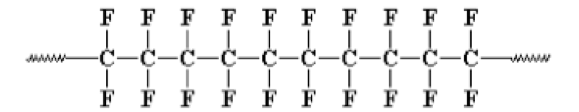
Fluorine atoms surround carbon atoms, creating a chemical structure that provides:
- Heat, electrical and chemical resistance
- Low coefficient of friction
- Non-stick characteristics
- Lubricity
Applications for PTFE Micropowders
PTFE micropowders offer a combination of unique properties that make them ideal for many applications.

Printing Inks
- Improves the rub resistance of printed stock better than conventional anti-scuff agents.
- Supports quick solvent release, faster printing speeds, and excellent print gloss.
- Enhances preparation of offset, heat-set, gravure, and flexographic inks.
- Reduces blockage in inkjets for increased efficiency and reduced waste.
- Easily disperses at room temperature for cheaper and more efficient processing.
Thermoplastic compounds
- Improves surface wear properties of plastics by decreasing friction between parts for maximum wear resistance.
- PTFE-filled thermoplastics include gears, bearings, wear plates, instrument components, and liners.

Elastomer compounds
- Improves mold release and wear resistance of rubber products due to low friction coefficient
- Enhances tear strength.
- Alternative to wax or state fillers that typically possess a limited life due to leaching when contacting hydraulic fluids or lubricating oils
Specialized oils and greases
- Water repellency reduces corrosion to extend equipment.
- Improves lubrication in applications with extreme pressure, temperatures, and environments.
- Used in applications where conventional additives such as graphite and molybdemun are unsuitable
- PTFE powder with grease, rosin, and mineral oil, can yield high-quality lubricants, which are widely used in ball bearings, wear-resistant bearings, lubricating guideways, sliding rods, open gears, chemical equipment valves,
- Offers cleanliness for greases used in the food, pharmaceutical, and dairy products.
Paint compounds
- Increases surface abrasion resistance when added to masonry, aircraft, and marine paints.
- Water repellency enables painted surfaces to be cleaned without removing the coating.
- Reduces flammability and improves paint’s spreading rate.
- Reduces fouling and marine growth on boat hulls due to non-stick properties.
Coatings and Finishes
- Improves surface lubrication and scuff resistance of many industrial finishes.
- Corrosion and abrasion resistance
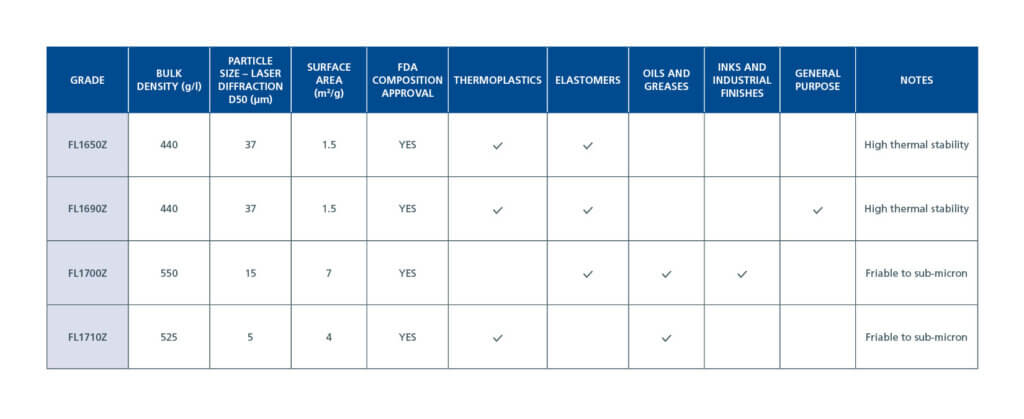
PTFE Micropowder Grades
Fluon® PTFE micropowders are developed in different grades to meet the specific needs of different applications. For instance:
- Printing inks and industrial finishes require a PTFE lubricant powder grade with the lowest surface area and porosity.
- Thermoplastics require a grade with high thermal stability.
- For Ink coatings used on metal cans, the grade should be FDA-approved for contact with food and drink.
- Oils, greases, and elastomers need a PTFE that withstands extreme pressures.
The molecular weight and particle size of Fluon® PTFE micropowders can be custom-tailored to yield optimal application-specific improvements for wear, friction, and pressure-velocity.
Overview
PTFE, a synthetic fluoropolymer with a low coefficient of friction, is ideal for non-stick applications. It is also resistant to water, heat, electricity, and friction, and can improve the strength and durability of thermoplastic and elastomer products. PTFE micropowders can enhance the performance of inks, coatings, oils, and greases. Different grades of PTFE micropowders are available to meet specific application needs. The molecular weight and particle size of the micropowders can be customized to yield optimal improvements for wear, friction, and pressure-velocity.
For more information on Fluon PTE Micropowders, visit PTFE Resins – AGC Chemicals or contact us at 800-424-7833.
 English
English